


You must be familiar with GxP referring to the ‘good practice’ guidelines and regulations ensuring that food, medical devices, drugs, and other life science products are safe, and of high quality. Good Documentation Practices (GDocP) is one such GxP applicable to the pharmaceutical and medical device industries.
Thoroughly grasping GDocP is paramount for relevant enterprises as it describes a globally recognized standard for the creation, management, and maintenance of reliable and accurate documents. Thus, GDocP emerges as a non-negotiable element of any pharmaceutical quality system (PQS) and quality risk management (QRM).
GDocP, also known as Good Recordkeeping Practice (GRK), is a set of protocols to ascertain informational validity and compliance with regulatory requirements in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. GDocP welcomes a robust quality assurance system which is mandatory for organizations operating in these highly regulated sectors.
Different regional regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, the EMA in Europe, the WHO, Health Canada, and the TGA in Australia, have established comprehensive documentation requirements to adhere to Good Documentation Practices (GDocP). While some GDocP standards are codified by authorities, others are not but are considered part of cGMP, with an emphasis on “current.” They ensure that all records are precise, complete, timely, legible, traceable, and properly controlled.
Non-compliance with these mandates can lead to severe consequences, including regulatory penalties and fines, product recalls, and patient safety risks. Regulatory bodies can issue warning letters, suspend operations, or impose hefty fines. Furthermore, poor documentation can compromise product quality, leading to recalls and patient harm, while non-compliance to damage a company’s reputation, loss of licenses, and fraud charges. This underscores the critical importance of complying with GDocP to ensure patient safety and maintain the integrity of pharmaceutical products as well as medical devices.
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

The core principles of GDocP, known as the ALCOA+ principles, state that all documentation should be:
Applying these aspects appropriately across all applicable areas of GMP and GDP activities, along with other supporting elements of a PQS, ensures the reliability of the information used to make critical decisions regarding medicinal products.
The manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical products and medical devices involve distinct procedures and respective documents documenting them.
SOP documents outline the essential processes and protocols that must be followed to ensure product quality and regulatory compliance.
QMS documentation provides a structured framework for managing quality policies, procedures, and processes within the organization.
These records necessitate GDocP compliance to maintain traceability and control of manufacturing processes and product history.
These documents capture the data and observations from laboratory experiments and testing, ensuring authenticity and reproducibility of results.
These reports document any deviations from standard processes and the corrective and preventive actions taken to address them.
Training records track the qualifications and training history of employees to ensure they are competent to perform their assigned tasks, within the regulated environments.
Like every other GxP, establishing a GDocP system should comprise well-defined steps covering document lifecycle management.
1. Establish a Documentation Policy
Develop a clear GDocP policy outlining objectives, scope, and applicability to ensure consistent documentation across all processes.
2. Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Create and standardize SOPs for document creation, review, approval, distribution, and archiving using approved templates.
3. Document Creation and Review
Ensure all documents are accurate, complete, legible, and traceable, with proper recording of data and details like dates and signatures.
4. Document Approval and Distribution
Set up a thorough review and approval process involving authorized personnel, and control the distribution of documents to maintain current versions.
5. Record Keeping and Archiving
Store records securely, define retention periods in compliance with regulations, and ensure easy accessibility for authorized personnel.
6. Regular Audits and Reviews
Conduct regular internal audits to verify GDocP compliance, identify areas for improvement, and implement continuous enhancements.
7. Handling Deviations and Corrections
Document, investigate, and correct any deviations from procedures, preserving original entries and preventing recurrence.
8. Documentation Culture
Foster a culture that values proper documentation as critical to manufacturing excellence, with strong leadership support for GDocP.
9. Electronic Documentation Systems
Utilize electronic documentation systems to streamline document control, improve accessibility, and ensure data integrity and regulatory compliance.
10. Training and Awareness
Provide comprehensive training to all employees on GDocP principles, with regular updates to maintain awareness and compliance.
Looking ahead, the future trends in GDocP are increasingly leaning towards digital documentation and electronic records, driven by the need to enhance efficiency in record-keeping. The transition from paper to electronic documentation represents a pivotal shift, as organizations aim to revamp operations and boost regulatory compliance.
However, implementing GDocP faces several challenges, including but not limited to data security concerns, the need for validation processes, and the integration of new systems with legacy infrastructure. Overcoming these hurdles is a front-runner for harnessing the full potential of a seamless and compliant GDocP system.
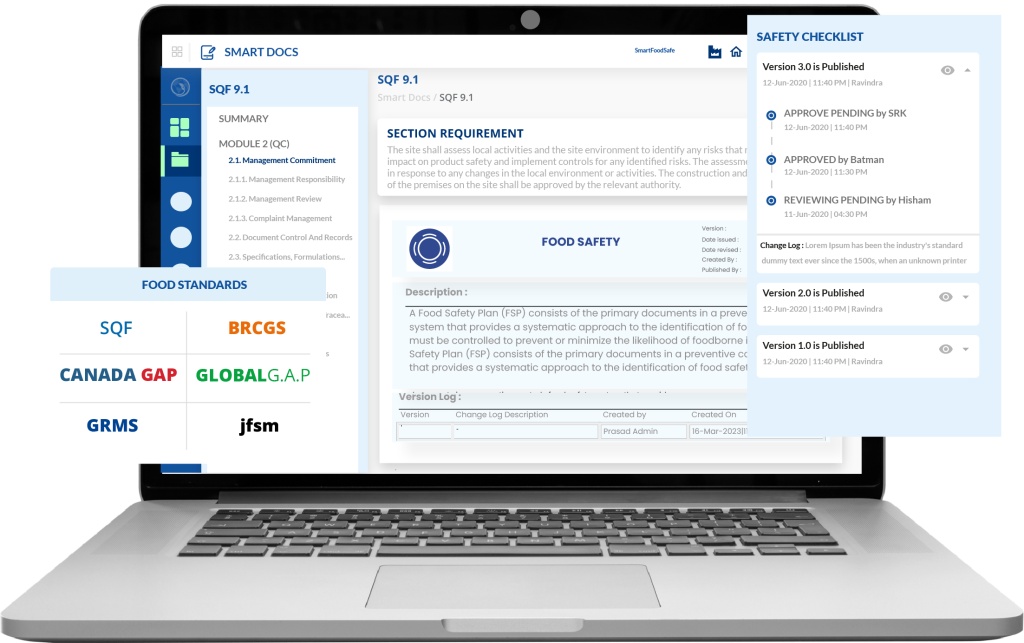
Smart Food Safe’s Smart Docs is a document compliance software solution instrumental for businesses seeking to digitally strategize and enforce good documentation practices (GDocP). We present a centralized document management system to bring efficient document control and transparency by tackling the multiple challenges hindering GDocP implementation. Let’s dive into how Smart Docs make this possible.
You must be familiar with GxP referring to the ‘good practice’ guidelines and regulations ensuring that food, medical devices, drugs, and other life science products are safe, and of high quality. Good Documentation Practices (GDocP) is one such GxP applicable to the pharmaceutical and medical device industries.
Thoroughly grasping GDocP is paramount for relevant enterprises as it describes a globally recognized standard for the creation, management, and maintenance of reliable and accurate documents. Thus, GDocP emerges as a non-negotiable element of any pharmaceutical quality system (PQS) and quality risk management (QRM).
GDocP, also known as Good Recordkeeping Practice (GRK), is a set of protocols to ascertain informational validity and compliance with regulatory requirements in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. GDocP welcomes a robust quality assurance system which is mandatory for organizations operating in these highly regulated sectors.
Different regional regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, the EMA in Europe, the WHO, Health Canada, and the TGA in Australia, have established comprehensive documentation requirements to adhere to Good Documentation Practices (GDocP). While some GDocP standards are codified by authorities, others are not but are considered part of cGMP, with an emphasis on “current.” They ensure that all records are precise, complete, timely, legible, traceable, and properly controlled.
Non-compliance with these mandates can lead to severe consequences, including regulatory penalties and fines, product recalls, and patient safety risks. Regulatory bodies can issue warning letters, suspend operations, or impose hefty fines. Furthermore, poor documentation can compromise product quality, leading to recalls and patient harm, while non-compliance to damage a company’s reputation, loss of licenses, and fraud charges. This underscores the critical importance of complying with GDocP to ensure patient safety and maintain the integrity of pharmaceutical products as well as medical devices.
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.


The core principles of GDocP, known as the ALCOA+ principles, state that all documentation should be:
Applying these aspects appropriately across all applicable areas of GMP and GDP activities, along with other supporting elements of a PQS, ensures the reliability of the information used to make critical decisions regarding medicinal products.
The manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical products and medical devices involve distinct procedures and respective documents documenting them.
SOP documents outline the essential processes and protocols that must be followed to ensure product quality and regulatory compliance.
QMS documentation provides a structured framework for managing quality policies, procedures, and processes within the organization.
These records necessitate GDocP compliance to maintain traceability and control of manufacturing processes and product history.
These documents capture the data and observations from laboratory experiments and testing, ensuring authenticity and reproducibility of results.
These reports document any deviations from standard processes and the corrective and preventive actions taken to address them.
Training records track the qualifications and training history of employees to ensure they are competent to perform their assigned tasks, within the regulated environments.
Like every other GxP, establishing a GDocP system should comprise well-defined steps covering document lifecycle management.
1. Establish a Documentation Policy
Develop a clear GDocP policy outlining objectives, scope, and applicability to ensure consistent documentation across all processes.
2. Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Create and standardize SOPs for document creation, review, approval, distribution, and archiving using approved templates.
3. Document Creation and Review
Ensure all documents are accurate, complete, legible, and traceable, with proper recording of data and details like dates and signatures.
4. Document Approval and Distribution
Set up a thorough review and approval process involving authorized personnel, and control the distribution of documents to maintain current versions.
5. Record Keeping and Archiving
Store records securely, define retention periods in compliance with regulations, and ensure easy accessibility for authorized personnel.
6. Regular Audits and Reviews
Conduct regular internal audits to verify GDocP compliance, identify areas for improvement, and implement continuous enhancements.
7. Handling Deviations and Corrections
Document, investigate, and correct any deviations from procedures, preserving original entries and preventing recurrence.
8. Documentation Culture
Foster a culture that values proper documentation as critical to manufacturing excellence, with strong leadership support for GDocP.
9. Electronic Documentation Systems
Utilize electronic documentation systems to streamline document control, improve accessibility, and ensure data integrity and regulatory compliance.
10. Training and Awareness
Provide comprehensive training to all employees on GDocP principles, with regular updates to maintain awareness and compliance.
Looking ahead, the future trends in GDocP are increasingly leaning towards digital documentation and electronic records, driven by the need to enhance efficiency in record-keeping. The transition from paper to electronic documentation represents a pivotal shift, as organizations aim to revamp operations and boost regulatory compliance.
However, implementing GDocP faces several challenges, including but not limited to data security concerns, the need for validation processes, and the integration of new systems with legacy infrastructure. Overcoming these hurdles is a front-runner for harnessing the full potential of a seamless and compliant GDocP system.
Smart Food Safe’s Smart Docs is a document compliance software solution instrumental for businesses seeking to digitally strategize and enforce good documentation practices (GDocP). We present a centralized document management system to bring efficient document control and transparency by tackling the multiple challenges hindering GDocP implementation. Let’s dive into how Smart Docs make this possible.

Signup to receive latest news, insights and updates docs Management